網路上有人分享bit font用法
https://www.pixiplayground.com/#/edit/zx72y62OBKjx76xs49UdF
來源:
https://discord.com/channels/734147990985375826/734150275467706510/1295765154289680536
Month: October 2024
Enable Node.js
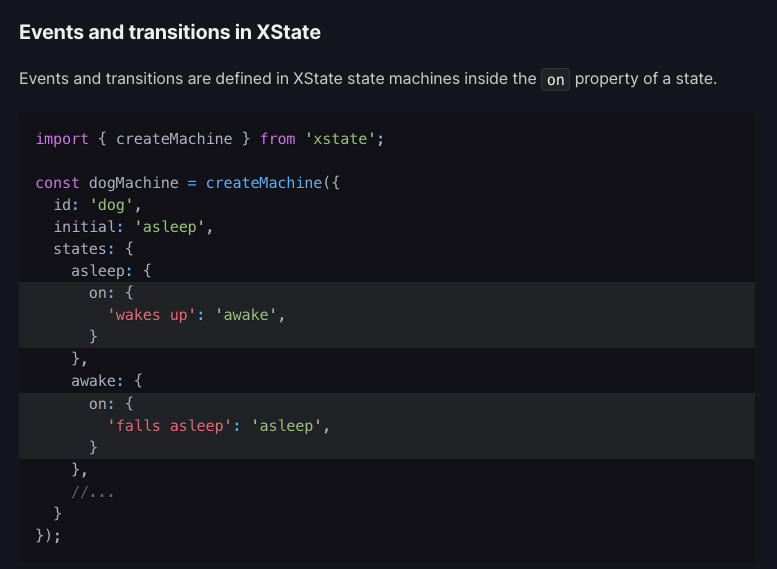
Learning XState
給予寬度,算出圖片等比例高度
Here’s a simple JavaScript example to calculate the proportional height of an image when you set a fixed width:
function calculateProportionalHeight(originalWidth, originalHeight, newWidth) {
const newHeight = (originalHeight * newWidth) / originalWidth;
return newHeight;
}
// Example usage:
const originalWidth = 800;
const originalHeight = 600;
const newWidth = 400;
const newHeight = calculateProportionalHeight(originalWidth, originalHeight, newWidth);
console.log(`The proportional height for the new width is: ${newHeight}px`);Explanation
- The
calculateProportionalHeightfunction takes the original width, original height, and the new width as arguments. - It calculates the new height using the formula we discussed and returns it.
In this example, if the original dimensions are 800×600, and you set a new width of 400, the function will calculate the new height that maintains the image’s aspect ratio.
https://chatgpt.com/share/6708fb61-3764-8001-b612-cc70253e169e
等比例縮放的圖
The goal is to make the sprite fit the width of the screen while keeping its proportions (aspect ratio) the same. To do this, we use the formula:
this.scale.x = this.app.screen.width / this.texture.width;and
this.scale.y = this.scale.x;What Does the Formula Mean?
Let’s break down the formula into simpler parts:
this.app.screen.width: This is the width of your app’s screen (the space in which your sprite should fit).this.texture.width: This is the original width of your sprite’s image.
When you divide this.app.screen.width by this.texture.width, you are calculating how much bigger or smaller the sprite should be to fit the screen.
Mathematical Principle
The principle behind this is called proportional scaling. The idea is that if you want to change the size of an object while keeping its shape the same, you need to multiply both the width and height by the same number.
Example in Simple Terms
Imagine you have a picture that is 200 pixels wide and your screen is 800 pixels wide. To make the picture fit the screen:
- You need to make the picture 4 times larger because
800 / 200 = 4.
That means the scale factor is 4, so you set:
this.scale.x = 4;
this.scale.y = 4;This makes both the width and the height of the picture 4 times bigger, keeping its original shape.
Why Use this.scale.x and this.scale.y?
Using this.scale.x and this.scale.y ensures that your sprite grows or shrinks evenly in all directions, so it doesn’t look stretched or squished.
Here’s a step-by-step summary of what happens:
- Calculate the scale factor:
this.app.screen.width / this.texture.width
- This tells you how much to multiply the width by to make it fit.
- Apply the scale factor to both dimensions:
- Set
this.scale.xto this value so the width fits the screen. - Set
this.scale.yto the same value to maintain the aspect ratio.
Real-Life Analogy
Think of a photo that you want to print in a larger size. If you want to make the photo twice as wide, you also need to make it twice as tall to keep it looking right. If you don’t do this, the picture might end up looking stretched or distorted.
I hope this breakdown helps you understand the math and logic behind scaling in PixiJS! If you have any more questions, feel free to ask! 😊